Enhancing asset visibility, operational efficiency, and decision-making across power, water and wastewater networks.
GIS is transforming how utility networks are planned, operated, and maintained
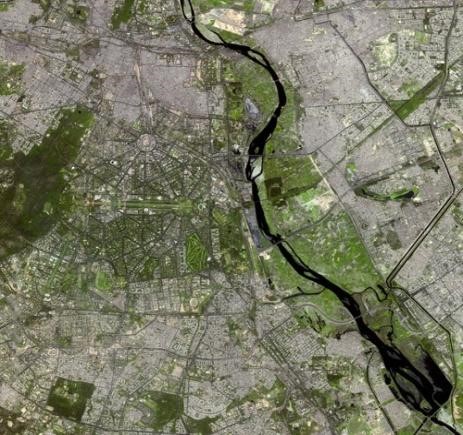
Geographic Information Systems (GIS) provide utilities with a unified spatial platform to map assets, analyze infrastructure performance, manage field operations, and respond quickly to outages or network disruptions.
By integrating data from pipelines, equipment, and the environment, this technology helps utilities modernize infrastructure, improve service reliability, and build resilience against climate and operational risks.


Overview
GIS Applications in Utilites
Our GIS-based utility solutions help streamline workflows, reduce operational costs, and enhance service reliability across water, power, and gas networks.
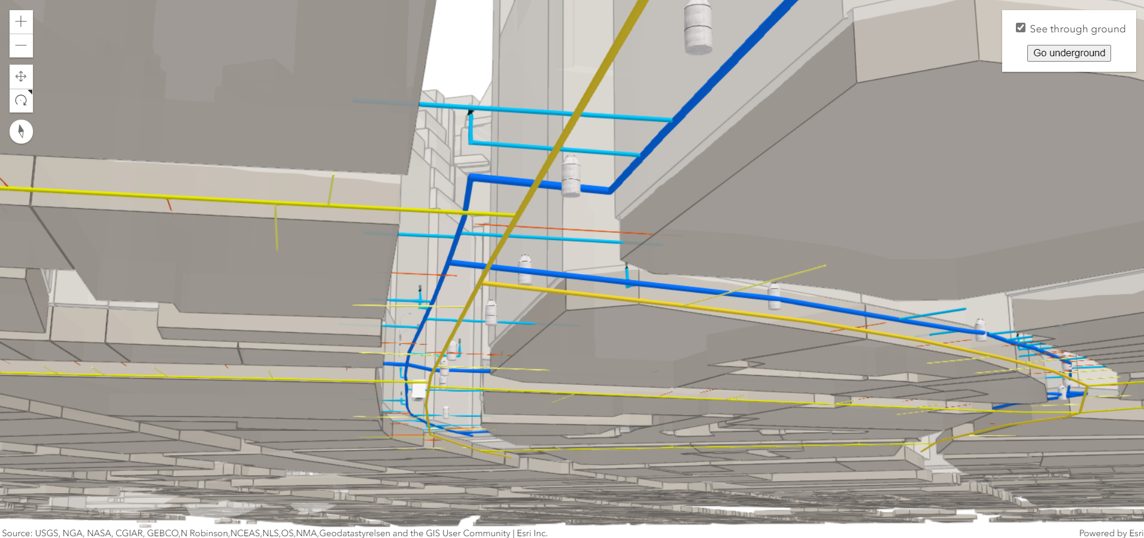
We utilize advanced geospatial data collection technologies such as LiDAR, remote sensing, drone surveys, satellite imagery, and field GPS to build highly accurate spatial databases for utility networks.
Our Works
We deliver end-to-end GIS solutions that help utility providers manage their networks with accuracy, efficiency, and real-time spatial intelligence.
What We Offer
Asset & Infrastructure Management
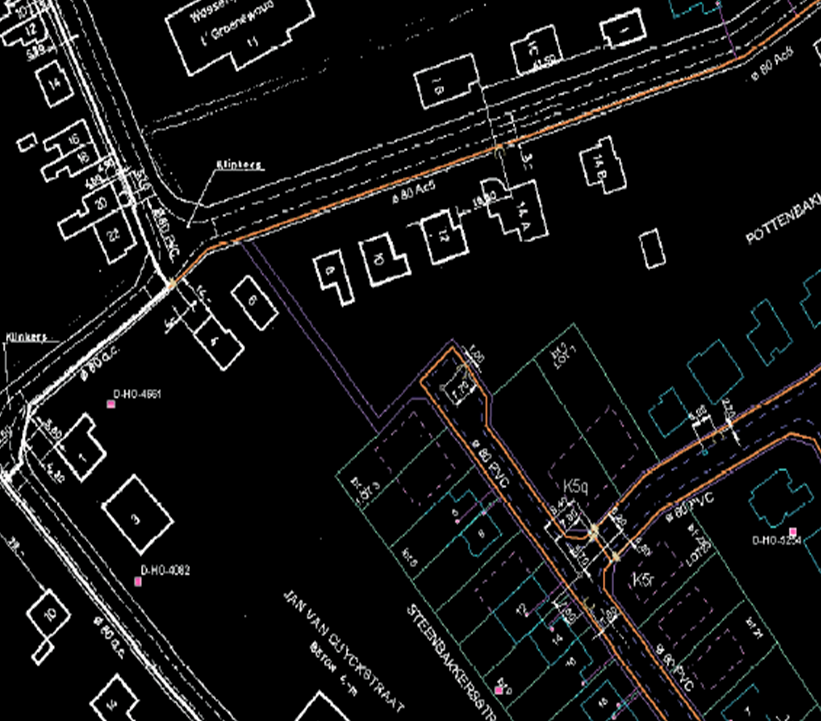
Asset Mapping & Digitization: Converting paper maps, CAD drawings, and satellite imagery into a digital GIS database.
Field Asset Inventory Surveys: deploying field crews to physically locate, tag, and verify utility assets and their attributes.
Data Conflation & Migration: Merging data from disparate sources to ensure the map matches reality.
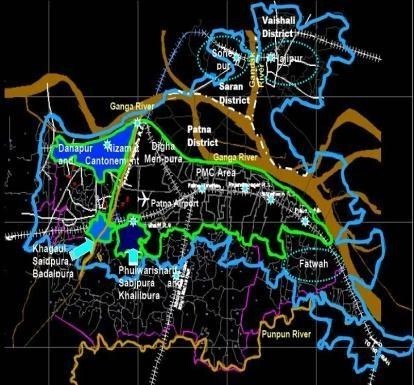
Land Base Creation: Creating base maps including land parcels, roads, and topography.


Network Planning & Engineering
Route Alignment & Corridor Analysis: Find the optimal path for new transmission lines or pipelines by analyzing terrain, land ownership, environmental impact, and costs.
Network Design & Optimization: Assisting engineers in assets placement to maximize coverage and minimize loss.
Site Suitability Analysis: Identifying the best locations for new facilities based on analysis.
Right-of-Way (RoW) Management: Managing the legal boundaries and vegetation clearance zones required around pipelines and power lines.
Operations & Maintenance (O&M)
Outage Management System (OMS) Integration: Integrating GIS with OMS to visualize power outages in real-time, predict the likely location of the fault, and group customer calls.
Mobile Workforce Management: Providing field crews for navigation, work order management, and real-time status reporting.
Vegetation Management: Using satellite or LiDAR data to identify trees encroaching on power lines and prioritizing tree-trimming schedules to prevent outages.
Inspection & Maintenance Dashboards: Creating operational dashboards that show executives the real-time health of the network.


Customer & Commercial Services
Consumer Indexing: The process of mapping every customer meter and linking it logically to the specific transformer or pipe segment that serves them.
Energy Audit & Loss Calculation: Using the CI data to calculate “Technical vs. Commercial” losses by comparing the energy supplied to a transformer against the total energy billed to the connected customers.
New Connection Planning: Automating the feasibility check for new customer connections.
Advanced & Emerging Solutions
Digital Twins: Creating a dynamic virtual replica of the physical grid that updates in real-time, allowing for simulation of scenarios.
Predictive Maintenance: Using historical GIS data and AI to predict which assets are likely to fail next.
Renewable Energy Integration: Modeling the impact of distributed energy resources on the grid load.